- HOME
- Applications
- Blog
- RF Cables Major Characteristics, Applications and Key Points for Selection
RF Cables Major Characteristics, Applications and Key Points for Selection
25-02-08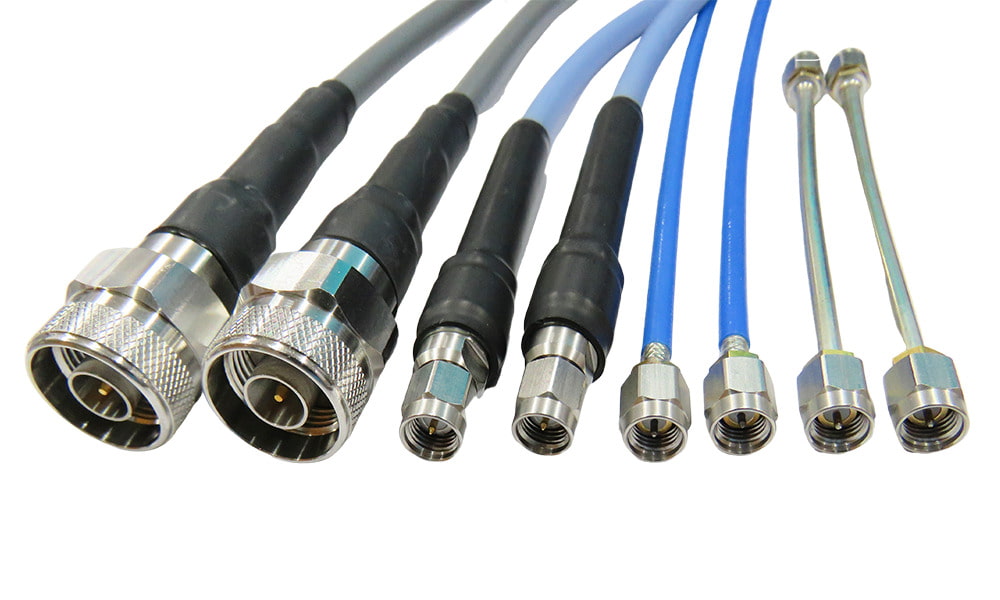
RF Cables are an essential component in modern communications equipment, responsible for transmitting high frequency signals and ensuring the stability and reliability of communications. With the advancement of technology, RF cables are used in a wide range of applications, from wireless networks to satellite communications, and even in smart devices. How to choose the right RF cable is directly related to the performance of the system. This article provides an in-depth look at the key features of RF cables, including structure, transmission efficiency and durability, as well as purchasing advice to help readers select the best RF cable product for their specific needs.
< Extended reading: Understanding Hermetic Sealing Technology and Hermetic Connectors in RF Applications >
What are RF Cables?
RF cables are cables specifically designed for the transmission of high frequency signals and are widely used in modern communications, broadcasting, radar and other equipment requiring high frequency signal transmission. Its main function is to transmit radio frequency waves from the source to the receiver in a stable manner, and to ensure the integrity and stability of the signal.
< Extended reading: What are RF Connectors? >
Working Principle of RF Cable
The operating principle of RF cables is based on the characteristics of high frequency signals traveling through the cable. RF signals are transmitted along the cable in the form of electromagnetic waves, and the structure of the cable is designed to effectively control signal loss and interference. RF cables are designed with specialized structures and materials to achieve stable transmission of high frequency signals. The following are some of the key principles and characteristics of RF cables:
-
Transmission of Electromagnetic Waves through Conductors
RF signals are transmitted in the form of electromagnetic waves in RF cables by means of a conductor that carries the signal from the input to the output.
The design of the RF cable ensures that the signal is transmitted over long distances with minimal attenuation and distortion. -
Impedance Matching
RF cables have a precise characteristic impedance (e.g., 50 ohms or 75 ohms) that matches the impedance of the transmission equipment.
Impedance matching reduces signal reflection, improves transmission efficiency, and ensures the integrity of the high frequency signal. -
Reduce Signal Loss
High frequency signal transmission is susceptible to attenuation. RF cables are designed with low loss materials and precision structures to minimize energy loss. This allows the high frequency signal to maintain its strength and quality over long distances. -
Masking of External Interference
Shielding design of RF cables can effectively block external electromagnetic interference and prevent the signal from being affected by noise.
Especially in high frequency environments, shielding is critical to ensure signal stability. -
Control of electromagnetic wave propagation characteristics
Structure of the RF cable is designed to precisely control the propagation path of electromagnetic waves, minimizing signal crosstalk and internal losses.
This allows the cable to efficiently transmit RF signals and achieve stable performance even in complex high frequency applications
< Extended reading: Explore Microwave Frequency and Their Applications in RF Microwave Connectors >
What are the main structures of RF Cables?
The basic structure of a common RF cable consists of conductor, dielectric layer, shielding layer and an outer jacket.
The following is the description for the main structures of RF cables:
Main structure table of RF cable
|
Structure |
Functions and descriptions |
|---|---|
|
Conductor |
It is mainly responsible for transmitting RF signals and is usually made of materials such as copper or aluminum with low resistance to reduce signal loss. |
|
Dielectric Layer |
Located between the conductor and the shielding layer, it is usually composed of an insulating material (such as polyethylene or PTFE), and its main function is to isolate the conductor and maintain the characteristic impedance of the cable. |
|
Shielding Layer |
Usually made of braided metal mesh, aluminum or copper foil, it is used to prevent external electromagnetic interference from entering the cable while preventing leakage of the signal inside the cable. |
|
Outer Cover |
The outermost protective layer, usually made of PVC or PE, is used to provide physical protection against abrasion, corrosion, and environmental influences to extend the service life of the cable. |
In addition, RF cables need to be used with RF coaxial cable connectors. RF coaxial cable connectors are mainly used for connecting all kinds of RF equipment to the cables, which are designed to ensure impedance matching and maintain stable signal transmission, minimize reflection and loss.
What are the Types of RF Cables? How are they Different from Normal Cables?
RF cables are designed for high frequency signal transmission and have the following major differences compared to normal cables:
Frequency Range
RF cables are capable of handling higher frequency signals, usually in the range of several hundred MHz to several GHz, and even up to tens GHz. Whereas ordinary cables are usually used for low frequency signals, and are unable to handle high frequency signal transmission effectively.
< Extended reading: What is mmWave? Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications! >
< Extended reading: Microwave Technology Principles and Applications >
Loss
RF cables are designed to minimize attenuation and loss of high frequency signals, which allows them to maintain higher signal quality during transmission. Ordinary cables transmit high frequency signals with greater loss, which can cause signal distortion or degradation.
Anti-Interference Performance
RF cables usually have a mask to protect the signal from external electromagnetic interference, which is one of the important characteristics. Ordinary cables lack this shielding and are susceptible to external electromagnetic interference, which can affect signal stability.
RF Cable Classification
RF cables can be categorized into different types according to their structure, purpose and application scenarios.
Below are the common classifications of RF cables and their structural features, applications and advantages:
Comparison of RF cables and other cables
|
Type |
Structural Features |
Scope of Application |
Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
|
RF Cables |
It consists of a center conductor, insulation, shield and outer jacket, and is commonly designed for 50 or 75 ohm impedance. |
Wireless communications, broadcasting, satellite communications, Internet connectivity |
Strong anti-interference, wide frequency range, low signal loss, suitable for high frequency transmission. |
|
Twisted Pair Cable |
Two insulated wires twisted together in a spiral pattern, usually used for low frequency signal transmission. |
LAN, telephone lines, data transmission |
Simple design and low cost, suitable for low frequency data transmission. |
|
Micro-strip Line |
It consists of a flat conductor, a dielectric layer, and a grounding layer, and is typically used on printed circuit boards (PCBs). |
High frequency circuit boards, wireless communication equipment, radar systems |
Precise control of signal transmission for integrated circuits and miniaturized designs. |
|
High Frequency Flat Cable |
It has a flat structure design, usually consisting of multiple parallel wires and is tightly constructed. |
High frequency instrument connection, high speed data transfer, internal computer connection |
Space saving, suitable for applications in small spaces, especially where high speed data transmission is required. |
How to Choose the Right RF Cables?
When selecting a suitable RF cable, the following key factors should be considered:
Frequency Range and Insertion Loss
(1) Frequency Range: The selection of RF cables should be based on the frequency range of the signals to be transmitted. Different types of RF cables cover different frequency ranges and should be selected to ensure that they can effectively transmit the desired high frequency signals.
(2) Insertion Loss: Insertion loss refers to the loss of signal as it travels through the cable, usually measured in decibels (dB). The lower the loss, the better the quality of the signal. Therefore, when choosing an RF cable, you should select one with lower loss, especially if you plan to use it for long distance transmission.
Impedance Matching
Impedance of RF cables is usually 50 ohm and 75 ohm. When choosing RF cables, make sure the impedance of the cables matches with the connected equipment (e.g. antenna, transmitter, receiver, etc.) to minimize reflections and maximize the efficiency of the signal transmission.
Durability
Durability should be considered when selecting RF cables, especially in harsh installation environments (e.g. high temperature, humidity, mechanical damage, etc.). Cables that are weather resistant, UV resistant, and chemical resistant will maintain stable performance over time.
Shielding Performance
The shielding layer of RF cables is the key part to prevent external interference from entering the cable and to prevent internal signal leakage. Selection of cables should be based on the application scenario and the masking performance. Especially in environments with strong electromagnetic interference, it is necessary to select cables with better masking performance, such as cables with double or multi-layer shielding design.
Usage Environment
According to the environment where the RF cable is to be used (e.g., indoor or outdoor, fixed installation or mobile use, etc.), select the appropriate cable material and design. For outdoor use, waterproof and corrosion-resistant designs are usually required.
Frequently Asked Questions about RF Cables
How to determine if an RF cable is suitable for a particular piece of equipment?
To determine whether an RF cable is suitable for a particular equipment, you should first check the impedance requirement of the equipment (usually 50 ohm or 75 ohm) and select a cable that matches it. At the same time, the frequency range and transmission loss of the RF cable should be examined to see if it meets the requirements of the equipment to ensure stable and efficient signal transmission. In addition, it is also important to select a cable that has the appropriate durability and interference resistance based on the environment in which the equipment will be used.
< Extended reading: How to Choose RF Blind Mating Connectors? >
What environmental conditions affect the performance of RF cables?
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, UV rays, chemicals and mechanical damage have a significant impact on the performance of RF cables. High temperatures, extreme low temperatures, and humidity can cause deterioration or damage to the cable's insulation, affecting the quality of the signal transmitted. Strong UV radiation and chemicals may also damage the cable's outer jacket, reducing its durability.
How are RF cables installed?
The installation method of RF cables should be chosen according to the usage environment and requirements. Generally speaking, avoid excessive bending or stretching of the RF cable as this will affect the signal transmission. Installation should avoid excessive mechanical load or pressure on the RF cable and ensure good shielding to get out the way of signal interference. For outdoor installation, waterproof and corrosion-resistant materials should be used to protect the cable.
How to connect the RF cable?
When connecting RF cables, it is necessary to ensure that the impedance of the connector matches perfectly with that of the RF cable and the equipment, so as to minimize signal reflection and transmission loss. It is recommended to use a suitable RF coaxial cable connector to achieve a stable connection, and take care to lock the connector tightly to ensure signal stability. For long distance transmission, the number of connectors should be minimized to reduce signal loss and interference risk.
< Extended reading: What is high frequency? High Frequency Features and Applications! >
Conclusion
RF cables play a pivotal role in modern communications technology, and their performance has a critical impact on the stability and efficiency of signal transmission. Choosing the right RF cables not only ensures the best performance of the equipment, but also effectively reduces loss and interference, and enhances the reliability of the overall system. Huang Liang Technologies specializes in the research and development and production of RF microwave connectors, and provides full support to customers with excellent quality and professional technology. We are pleased to provide RF cable selection consulting services to help you find the most suitable product solutions. For more information about our products and services, please feel free to contact us and we will endeavor to provide you with the best assistance!
< Extended reading: Microwave Communication: The Core Technology of Modern Technology and the Key Role of RF Connectors >