- HOME
- Applications
- Blog
- Microwave Adapter Essentials: Your Guide to Seamless RF Connections
Microwave Adapter Essentials: Your Guide to Seamless RF Connections
25-12-29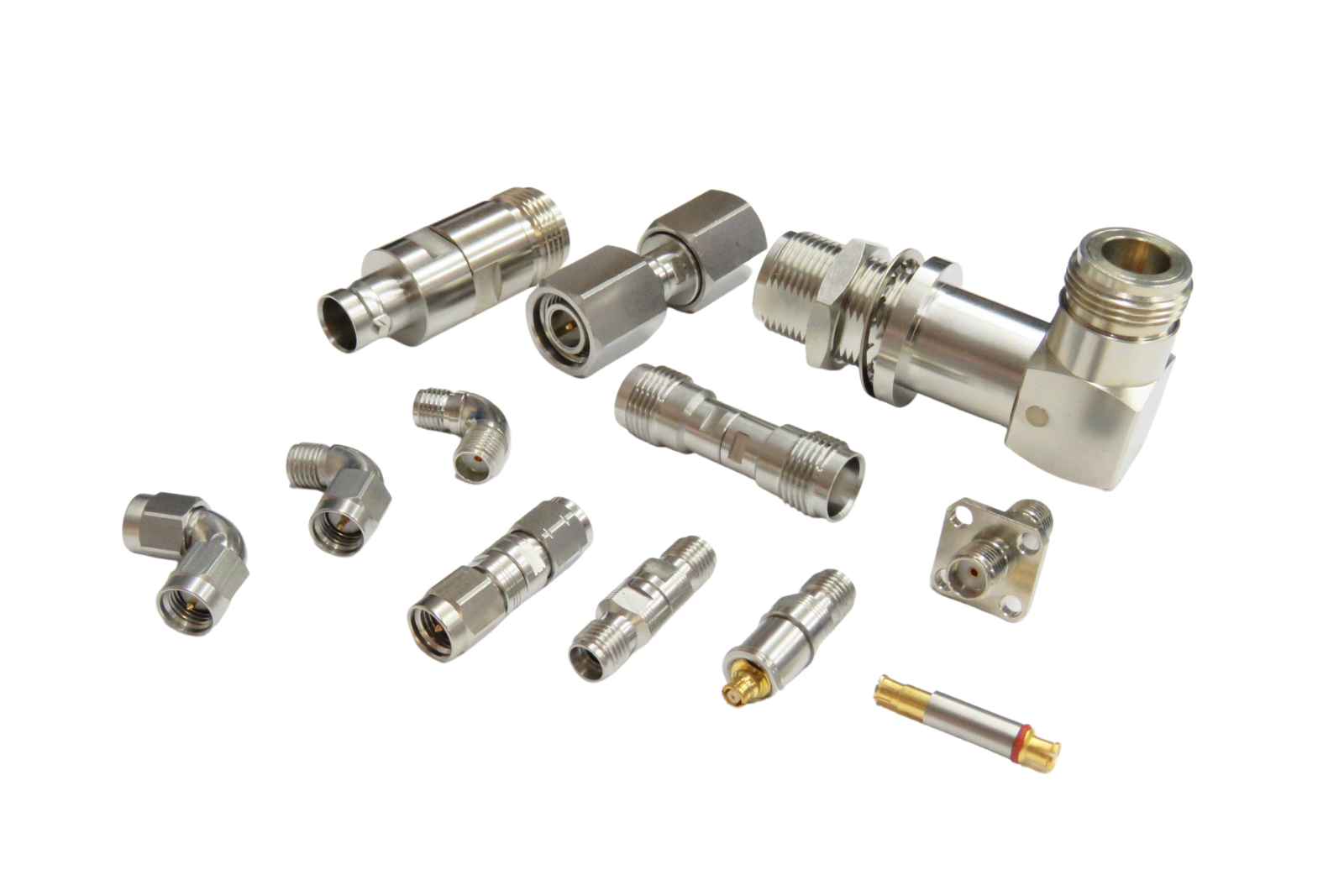
In modern high frequency communications and RF systems such as radar, satellite, and wireless testing, various devices often require different frequency ranges, connection interfaces, and transmission specifications for system operation. Microwave adapters play a critical bridging role here, effectively connecting connectors and components of different standards while ensuring complete signal transmission without distortion or loss. Therefore, microwave adapter has become indispensable critical components.
Microwave adapter design must simultaneously support wide bandwidth, low insertion loss, excellent impedance matching, and high frequency stability. Common types include adapters between interfaces such as SMA, N, 3.5mm, 2.92mm (K), 2.4mm, and 1.85mm (V), covering frequencies from DC up to 67 GHz and beyond. These microwave adapters enable engineers to flexibly integrate RF components and modules from different manufacturers or generations without compromising performance. They are also one of the core elements ensuring system consistency and signal integrity.
Role of Microwave Adapters in RF Systems
Microwave adapters serve several primary functions when used in RF systems.- Interface Transition
- Facilitating Frequency and Interface Transition (Legacy to Modern Compatibility)
- Signal Integrity Preservation
- Enhanced Impedance Matching
- Flexible Test Configuration
- System Integration Support
- Cost-Effective Maintenance
Microwave Adapter Types and Application Scenarios
Common microwave adapter types and application selection guidelines are as follows.- Classification by Microwave Adapter Interface
|
Type |
Description |
Applicable Range |
|---|---|---|
|
SMA to N |
Common for low-to-mid-frequency conversion (DC~18 GHz) Significant size difference between the two connectors. | Test instruments and antenna modules |
|
SMA to 2.92mm (K) |
High-frequency adapters (DC ~40 GHz) Similar in size to SMA but capable of high frequency. |
Precision testing, high-speed module interface |
|
SMA to 2.4mm/1.85mm |
Ultra-high-frequency adapters Supports 50 to 67 GHz frequency range. |
Millimeter-wave applications, advanced radar or satellite systems |
|
BNC to SMA |
BNC is a low-frequency (<4 GHz) adapter. SMA is a common connector for mid-to-high frequencies. |
General electronic testing, communication system transition interface |
|
TNC to SMA |
Used for outdoor waterproof equipment and indoor test equipment. | Communication base stations, wireless network equipment |
- Classification by Gender of Microwave Adapter
|
Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Plug to Jack |
The most common type, used for standard connections. |
|
Jack to Jack |
Used for extension or special testing requirements e.g., inline connections. |
- Classification of Microwave Adapters by Product Perspective and Structure
|
Type |
Description |
Applicaiton Scenario |
|---|---|---|
|
Straight |
Standard straight-through connection. | Suitable for most applications. |
|
Right Angle Adapter |
For use in space-constrained environments. | Compact modules, internal cabinet wiring. |
|
Bulkhead |
Mountable on chassis or panel walls. | Test panels, chamber structures. |
|
Panel Mount |
Mounted on test or equipment panels. | For instrument panel adapter holes. |
How to Select the Appropriate Microwave Adapter?
- Based on Frequency Requirements
- For applications below 18 GHz, such as general RF testing or commercial communications, traditional microwave adapters like SMA or N-type can be selected.
- For applications at 26.5 GHz, 40 GHz, 50 GHz, or 67 GHz, select high frequency microwave adapters such as 2.92mm (K), 2.4mm, 1.85mm (V), or 1.0mm (W).
- Consider Interface Pairing
- Confirm the connector types (interface and gender) used by both end devices and select the corresponding adapter.
- For example, if the device uses a SMA plug as well as the test lead is a 2.92mm jack, the selection would be SMA jack to 2.92mm plug adapter.
- Based on Physical Space Requirements
- For confined spaces, choose right-angle adapters. For board penetration or panel mounting, select bulkhead/panel mount styles.
- Select High Quality Adapters to Maintain Signal Integrity
- For high frequency (>26.5 GHz) adapters, prioritize low insertion loss and low VSWR. Selecting precision adapters minimizes signal reflection and instability.
- Avoid Excessive Adapter Cascading
- Each Microwave Adapter introduces additional loss. Directly select the required interface adapter to avoid multi-stage cascading.
Microwave Adapter Performance Parameters
Key Performance Indicators for Microwave Adapters are as below.|
Performance |
Description |
Evaluation Point/Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Insertion Loss |
Energy loss incurred when signals pass through connectors, measured in dB. Typically, lower values are preferable (<0.1 dB is ideal). | High loss causes signal attenuation, impacting system efficiency and sensing sensitivity. |
|
Return Loss |
The ratio of reflected energy, measured in dB. Higher values indicate less reflection (>20 dB is ideal). | Indicates impedance matching quality, preventing signal reflections that disrupt system stability |
|
VSWR |
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio, ideal value is 1.0:1, common specifications are <1.2 or <1.3. | Correlated with return loss, directly reflects impedance matching effectiveness. |
|
Opertating |
The frequency range over which the adapter operates stably, e.g., DC–18 GHz, DC–40 GHz, DC–67 GHz. | Must match the frequency bands used by the application system e.g., >50 GHz for millimeter-wave radar. |
|
Characterstics |
Typically 50 Ω or 75 Ω must match the system. | Mismatch causes reflections and signal distortion. |
|
Impedance |
Internal structure of the adapter must maintain stable impedance, mechanical errors must not cause abrupt impedance changes. | Affects high frequency signal integrity and phase stability. |
|
Dielectric |
The maximum voltage an adapter can withstand without breakdown, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of Vrms. | Critical for safety in high power or high voltage applications. |
|
Power |
The maximum continuous power it can handle, dependent on frequency and temperature rise (e.g., 10W, 50W, 100W). | Requires special attention in high power systems like radar or transmitters. |
|
Phase |
Requires minimal phase error for phase-sensitive applications e.g., phased array antennas. | Requires special attention in high and low temperature environments or for military specifications. |
|
Thermal |
Frequency response and mechanical dimensions should not exhibit significant variation with temperature. | Special attention is required for high-temperature/low-temperature environments or military specifications. |
|
Durability |
Mating cycles (e.g., >500 cycles), structural strength, corrosion resistance plating materials such as gold, nickel, etc. | Affects long-term reliability, critical for test equipment or industrial settings. |
|
Structure and Gender Types |
Plug/Jack, Straight/Right-Angle, Bulkhead, Panel Mount, etc. | Impact on actual assembly and spatial compatibility. |
Application Evaluation Recommendations for Personnel Requiring Microwave Adapters.
- R&D Engineers
Focus on frequency, insertion loss, phase, and impedance matching. Exercise particular caution in high-frequency (>26.5 GHz) or low-loss applications.
- Quality Assurance/Quality Engineers
Prioritize specification consistency, electrical test results (VSWR/RL), plating quality, and durability test reports.
- Purchasing Personnel
Ensure product model-specific frequency ratings, interface configurations, RoHS/REACH compliance, supplier certifications (e.g., ISO9001/AS9100), delivery schedules, and post-sales support.
Microwave Adapter of Huang Liang Technologies is engineered for Future Technologies
Huang Liang Technologies excels in four key points, technology, quality, production capacity/lead time, and application support.
- Technical Capabilities
- High Frequency Performance Control Capability
- Complete Product Lineup
- Simulation and Matching Capabilities
- Mating Durability and Structural Reliability Testing
- Customization Capabilities
- Quality Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- RoHS / REACH Compliance
- Reliability Test Reports
- Traceability
- Production Capacity and Delivery Capability
- Stable Supply Capability
- Fast Lead Times
- Engineering Support
- Provide 3D CAD / Electrical Models
- RF Design Consulting Capabilities
- Rapid Sample Support